[toc]
CentOS7一键安装OpenVPN
需求及使用场景
公司的一些资源不想对外开放访问,例如gitlab、jenkins等等,现在想要的效果是部分资源只允许公司公网IP以及特定IP访问,这个时候就需要用到VPN了,但是公司花钱买VPN是不可能的,那么就需要一款免费好用的VPN,OpenVPN免费开源又好用,配置完OpenVPN后再加上云主机的安全组就完美解决问题了。
说明
| 系统 | openvpn版本 | 内网IP | openvpn分配客户端网段 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CentOS7.9 | 2.4.11 | 10.206.0.9 | 10.8.0.0 |
1.安装OpenVPN
1.1 克隆项目
git clone https://github.com/Nyr/openvpn-install.git
1.2 执行安装脚本
cd openvpn-install && sh openvpn-install.sh
安装完成后再次执行脚本会提示如下
OpenVPN is already installed.
Select an option:
# 添加新的客户端
1) Add a new client
# 移除已存在的客户端
2) Revoke an existing client
# 移除OpenVPN
3) Remove OpenVPN
# 退出
4) Exit
Option:
第一步、输入本机私网IP地址
Welcome to this OpenVPN road warrior installer!
Which IPv4 address should be used?
1) 10.9.95.147
2) 172.17.0.1
3) 172.20.0.1
IPv4 address [1]: 1
第二步、输入本机公网IP
This server is behind NAT. What is the public IPv4 address or hostname?
Public IPv4 address / hostname [8.8.8.8]: 8.8.8.8
第三步、选择OpenVPN协议,推荐使用UDP
Which protocol should OpenVPN use?
1) UDP (recommended)
2) TCP
Protocol [1]: 1
第四步、输入OpenVPN监听的端口
What port should OpenVPN listen to?
Port [1194]:
第五步、为客户端选择一个DNS服务器
Select a DNS server for the clients:
1) Current system resolvers
2) Google
3) 1.1.1.1
4) OpenDNS
5) Quad9
6) AdGuard
DNS server [1]: 1
第六步、为第一个客户端输入一个名称
Enter a name for the first client:
Name [client]:
��第七步、按任意键开始安装
OpenVPN installation is ready to begin.
Press any key to continue...
完整输出
OpenVPN installation is ready to begin.
Press any key to continue...
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Determining fastest mirrors
10gen | 1.2 kB 00:00:00
base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
centosplus | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB 00:00:00
epel | 4.7 kB 00:00:00
extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
nginx-stable | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
zabbix | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
zabbix-non-supported | 951 B 00:00:00
(1/7): 10gen/primary | 32 kB 00:00:00
(2/7): extras/7/x86_64/primary_db | 222 kB 00:00:00
(3/7): epel/x86_64/updateinfo | 1.0 MB 00:00:00
(4/7): centosplus/7/x86_64/primary_db | 1.6 MB 00:00:01
(5/7): base/7/x86_64/primary_db | 6.1 MB 00:00:01
(6/7): updates/7/x86_64/primary_db | 3.7 MB 00:00:01
(7/7): epel/x86_64/primary_db | 6.9 MB 00:00:01
10gen 279/279
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package epel-release.noarch 0:7-13 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
========================================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
========================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
epel-release noarch 7-13 epel 15 k
Transaction Summary
========================================================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total download size: 15 k
Installed size: 25 k
Downloading packages:
epel-release-7-13.noarch.rpm | 15 kB 00:00:00
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : epel-release-7-13.noarch 1/1
warning: /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo created as /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.rpmnew
Verifying : epel-release-7-13.noarch 1/1
Installed:
epel-release.noarch 0:7-13
Complete!
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
Package 1:openssl-1.0.2k-19.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version
Package 2:tar-1.26-35.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package ca-certificates.noarch 0:2019.2.32-76.el7_7 will be updated
---> Package ca-certificates.noarch 0:2020.2.41-70.0.el7_8 will be an update
---> Package openvpn.x86_64 0:2.4.9-1.el7 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: libpkcs11-helper.so.1()(64bit) for package: openvpn-2.4.9-1.el7.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package pkcs11-helper.x86_64 0:1.11-3.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
========================================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
========================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
openvpn x86_64 2.4.9-1.el7 epel 524 k
Updating:
ca-certificates noarch 2020.2.41-70.0.el7_8 base 382 k
Installing for dependencies:
pkcs11-helper x86_64 1.11-3.el7 epel 56 k
Transaction Summary
========================================================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+1 Dependent package)
Upgrade 1 Package
Total download size: 962 k
Downloading packages:
Delta RPMs disabled because /usr/bin/applydeltarpm not installed.
(1/3): ca-certificates-2020.2.41-70.0.el7_8.noarch.rpm | 382 kB 00:00:00
(2/3): pkcs11-helper-1.11-3.el7.x86_64.rpm | 56 kB 00:00:00
(3/3): openvpn-2.4.9-1.el7.x86_64.rpm | 524 kB 00:00:00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 3.4 MB/s | 962 kB 00:00:00
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : pkcs11-helper-1.11-3.el7.x86_64 1/4
Installing : openvpn-2.4.9-1.el7.x86_64 2/4
Updating : ca-certificates-2020.2.41-70.0.el7_8.noarch 3/4
Cleanup : ca-certificates-2019.2.32-76.el7_7.noarch 4/4
Verifying : ca-certificates-2020.2.41-70.0.el7_8.noarch 1/4
Verifying : openvpn-2.4.9-1.el7.x86_64 2/4
Verifying : pkcs11-helper-1.11-3.el7.x86_64 3/4
Verifying : ca-certificates-2019.2.32-76.el7_7.noarch 4/4
Installed:
openvpn.x86_64 0:2.4.9-1.el7
Dependency Installed:
pkcs11-helper.x86_64 0:1.11-3.el7
Updated:
ca-certificates.noarch 0:2020.2.41-70.0.el7_8
Complete!
init-pki complete; you may now create a CA or requests.
Your newly created PKI dir is: /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus
....+++
...................................+++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
.................................................................+++
....+++
writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2726385.U7ScUb/tmp.FTK8rI'
-----
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2726385.U7ScUb/tmp.9FN60w
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
commonName :ASN.1 12:'server'
Certificate is to be certified until Nov 28 02:24:33 2030 GMT (3650 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
.....+++
........................................................................................+++
writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2726473.aJtBJi/tmp.bmyQVL'
-----
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2726473.aJtBJi/tmp.zwz1tQ
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
commonName :ASN.1 12:'pptfz'
Certificate is to be certified until Nov 28 02:24:34 2030 GMT (3650 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2726540.Fvyapy/tmp.eJmfVQ
An updated CRL has been created.
CRL file: /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/crl.pem
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn-iptables.service to /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn-server@server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/openvpn-server@.service.
Finished!
The client configuration is available in: /root/pptfz.ovpn
New clients can be added by running this script again.
:::tip说明
客户端文件是 /root/pptfz.ovpn ,在最后的输出中有提示,这里的客户端文件名称是自定义的,然后把这个文件下载到本地,后续配置VPN认证的时候需要用到这个客户端文件
:::
1.3 查看OpenVPN相关信息
1.3.1 查看OpenVPN进程
默认是以 nobody 用户运行,在 /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf 中可以自定义
$ ps aux|grep [o]penvpn
nobody 2726623 0.0 0.2 77168 4040 ? Ss 10:24 0:00 /usr/sbin/openvpn --status /run/openvpn-server/status-server.log --status-version 2 --suppress-timestamps --config server.conf
1.3.2 OpenVPN默认监听 udp 1194 端口
$ netstat -nupl|grep 1194
udp 0 0 10.9.95.147:1194 0.0.0.0:* 2726623/openvpn
1.3.3 查看版本
$ openvpn --version
OpenVPN 2.4.11 x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu [Fedora EPEL patched] [SSL (OpenSSL)] [LZO] [LZ4] [EPOLL] [PKCS11] [MH/PKTINFO] [AEAD] built on Apr 21 2021
library versions: OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017, LZO 2.06
Originally developed by James Yonan
Copyright (C) 2002-2018 OpenVPN Inc <sales@openvpn.net>
Compile time defines: enable_async_push=no enable_comp_stub=no enable_crypto=yes enable_crypto_ofb_cfb=yes enable_debug=yes enable_def_auth=yes enable_dependency_tracking=no enable_dlopen=unknown enable_dlopen_self=unknown enable_dlopen_self_static=unknown enable_fast_install=yes enable_fragment=yes enable_iproute2=yes enable_libtool_lock=yes enable_lz4=yes enable_lzo=yes enable_management=yes enable_multihome=yes enable_pam_dlopen=no enable_pedantic=no enable_pf=yes enable_pkcs11=yes enable_plugin_auth_pam=yes enable_plugin_down_root=yes enable_plugins=yes enable_port_share=yes enable_selinux=yes enable_server=yes enable_shared=yes enable_shared_with_static_runtimes=no enable_small=no enable_static=yes enable_strict=no enable_strict_options=no enable_systemd=yes enable_werror=no enable_win32_dll=yes enable_x509_alt_username=yes with_aix_soname=aix with_crypto_library=openssl with_gnu_ld=yes with_mem_check=no with_sysroot=no
2.配置OnenVPN使用账号密码认证
2.1 编辑脚本
:::tip说明
这个是现在公司线上用到的文件,目前没有找到出处,不知道为什么,总之就是利用一个存放用户名密码的自定义文件 /etc/openvpn/psw-file 来作为认证文件
编辑如下脚本,后续openvpn的配置文件 /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf 中会引用这个脚本
openvpn运行用户对于这个脚本至少有rx权限,否则认证会失败
:::
cat >> /etc/openvpn/checkpsw.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/sh
###########################################################
# checkpsw.sh (C) 2004 Mathias Sundman <mathias@openvpn.se>
#
# This script will authenticate OpenVPN users against
# a plain text file. The passfile should simply contain
# one row per user with the username first followed by
# one or more space(s) or tab(s) and then the password.
PASSFILE="/etc/openvpn/psw-file"
LOG_FILE="/etc/openvpn/openvpn-password.log"
TIME_STAMP=`date "+%Y-%m-%d %T"`
###########################################################
if [ ! -r "${PASSFILE}" ]; then
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: Could not open password file \"${PASSFILE}\" for reading." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
fi
CORRECT_PASSWORD=`awk '!/^;/&&!/^#/&&$1=="'${username}'"{print $2;exit}' ${PASSFILE}`
if [ "${CORRECT_PASSWORD}" = "" ]; then
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: User does not exist: username=\"${username}\", password=\"${password}\"." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
fi
if [ "${password}" = "${CORRECT_PASSWORD}" ]; then
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: Successful authentication: username=\"${username}\"." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 0
fi
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: Incorrect password: username=\"${username}\", password=\"${password}\"." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
EOF
赋予脚本执行权限
chmod +x /etc/openvpn/checkpsw.sh
2.2 修改openvpn配置文件 /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
2.2.1 追加以下内容
其中 auth-user-pass-verify 对应的文件一定要与上一步创建的脚本名相同
cat >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf << EOF
auth-user-pass-verify /etc/openvpn/checkpsw.sh via-env
verify-client-cert
username-as-common-name
script-security 3
EOF
/etc/openvpn/server/server.conf 文件默认内容
local 10.206.0.9
port 1194
proto udp
dev tun
ca ca.crt
cert server.crt
key server.key
dh dh.pem
auth SHA512
tls-crypt tc.key
topology subnet
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0
push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"
ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt
push "dhcp-option DNS 183.60.83.19"
push "dhcp-option DNS 183.60.82.98"
keepalive 10 120
cipher AES-256-CBC
user nobody
group nobody
persist-key
persist-tun
verb 3
crl-verify crl.pem
explicit-exit-notify
2.2.2 修改 server.conf
删除开头的 local 一行
sed -i.bak '1d' /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
2.3 重启服务
systemctl enable openvpn@server.service
systemctl restart openvpn-server@server
2.4 添加账号
后续的账号都在这个文件 /etc/openvpn/psw-file 中添加,用户名和密码以空格隔开,每行一个
# 用户名密码文件
cat > /etc/openvpn/psw-file << EOF
test test123
EOF
# 文件所有者一定要是openvpn运行的用户,��这里openvpn默认运行用户为nobody
chown nobody.nobody /etc/openvpn/psw-file && chmod 600 /etc/openvpn/psw-file
2.5 修改客户端文件
执行完一键安装脚本后会提示客户端文件位置
The client configuration is available in: /root/pptfz.ovpn
New clients can be added by running this script again.
客户端文件需要追加一行 auth-user-pass 内容,开启用户名密码认证,然后下载到本地
sed -i '14aauth-user-pass' /root/pptfz.ovpn
3.客户端安装配置
3.1 mac连接示例
这里以mac为例,我下载的是 Tunnelblick Tunnelblick github地址
安装完成后把客户端文件 pptfz.ovpn(文件名是自定义的) 拖入到 Tunnelblick
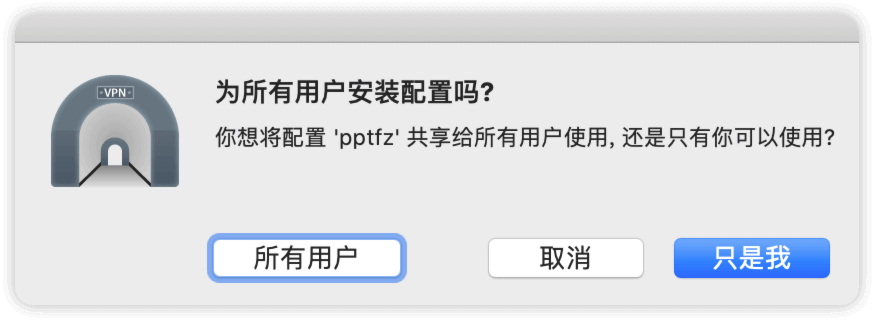
选择安装的用户
输入本机密码
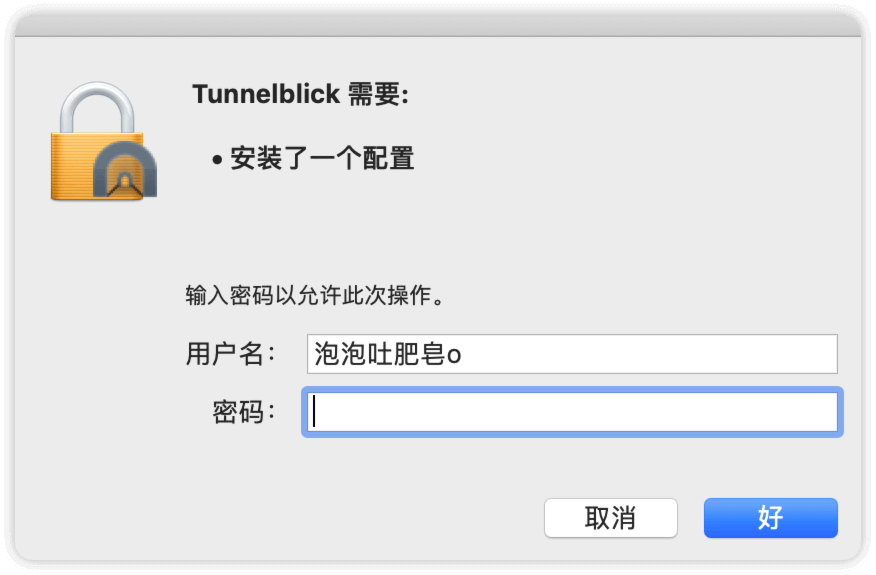
输入完成后会提示如下

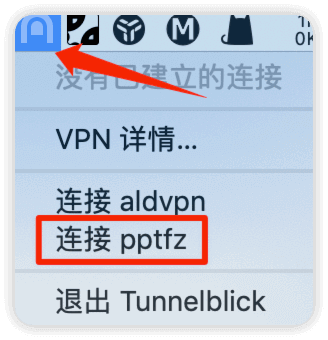
找�到相应图标,点击要连接的VPN
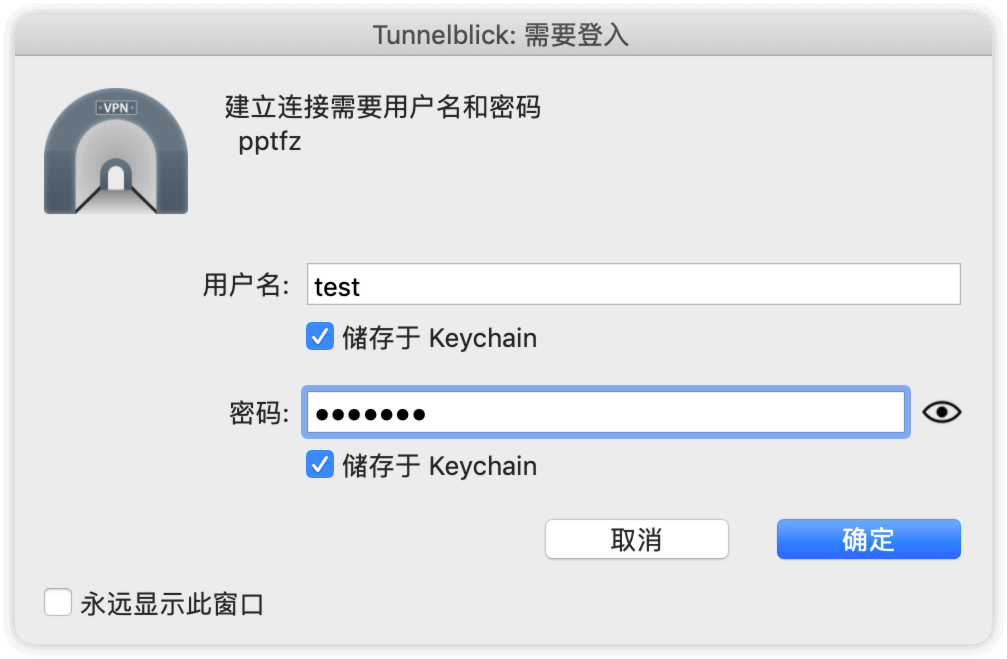
输入用户名和密码
连接成功

连接成功后,就会在本机生成一个 utun1 的虚拟网卡,并获取openvpn server.conf 中设置的 server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 给客户端分配的网段,IP地址从 10.8.0.2 开始分配
utun1: flags=8051<UP,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.8.0.2 --> 10.8.0.2 netmask 0xffffff00
此时mac本机是能与服务器内网相互ping通的
mac本机ping服务器内网
$ ping -c2 10.206.0.9
PING 10.206.0.9 (10.206.0.9): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 10.206.0.9: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=90.547 ms
64 bytes from 10.206.0.9: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=63.691 ms
--- 10.206.0.9 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 63.691/77.119/90.547/13.428 ms
服务器ping mac本机
$ ping -c2 10.8.0.2
PING 10.8.0.2 (10.8.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=85.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=90.3 ms
--- 10.8.0.2 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1000ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 85.362/87.876/90.390/2.514 ms
3.2 windows连接示例
windows安装就是一路下一步
导入客户端文件
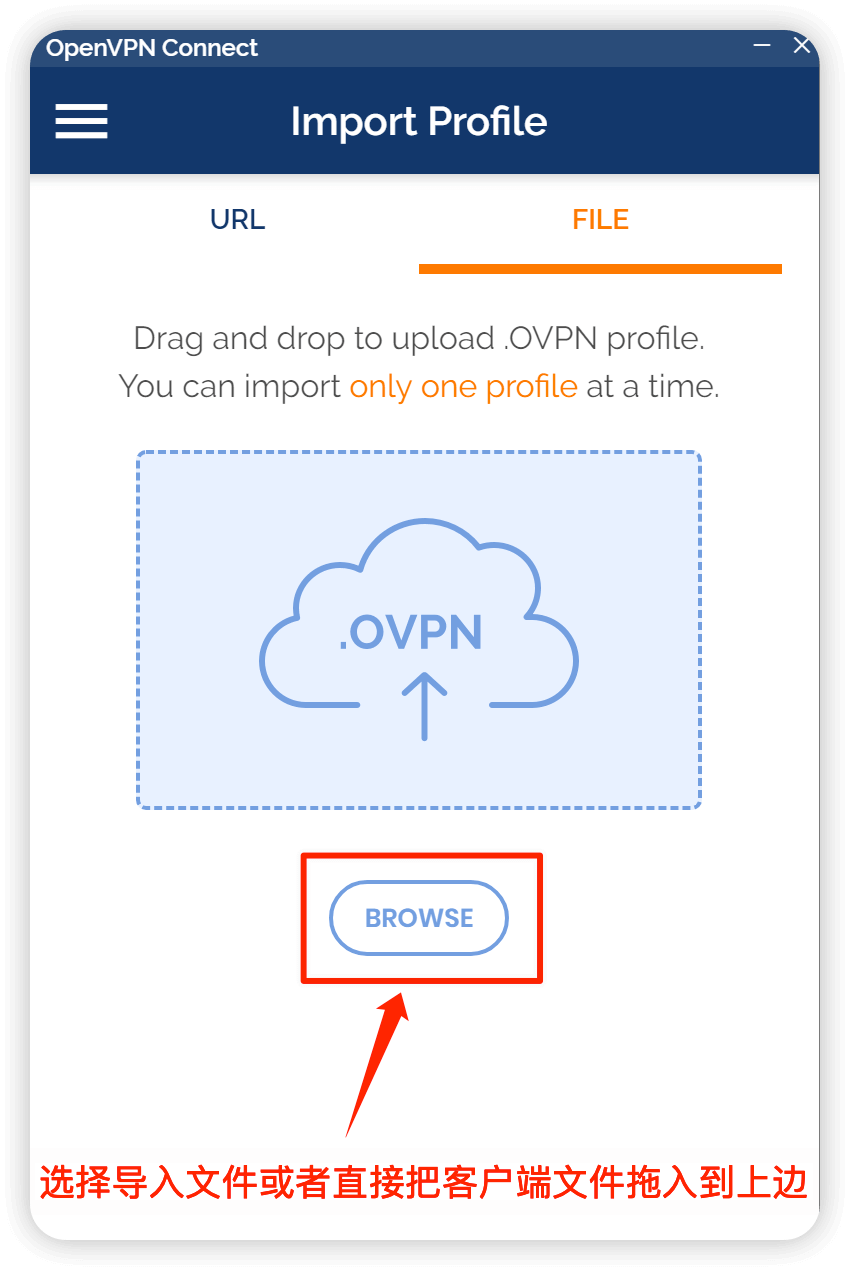
输入用户名和密码

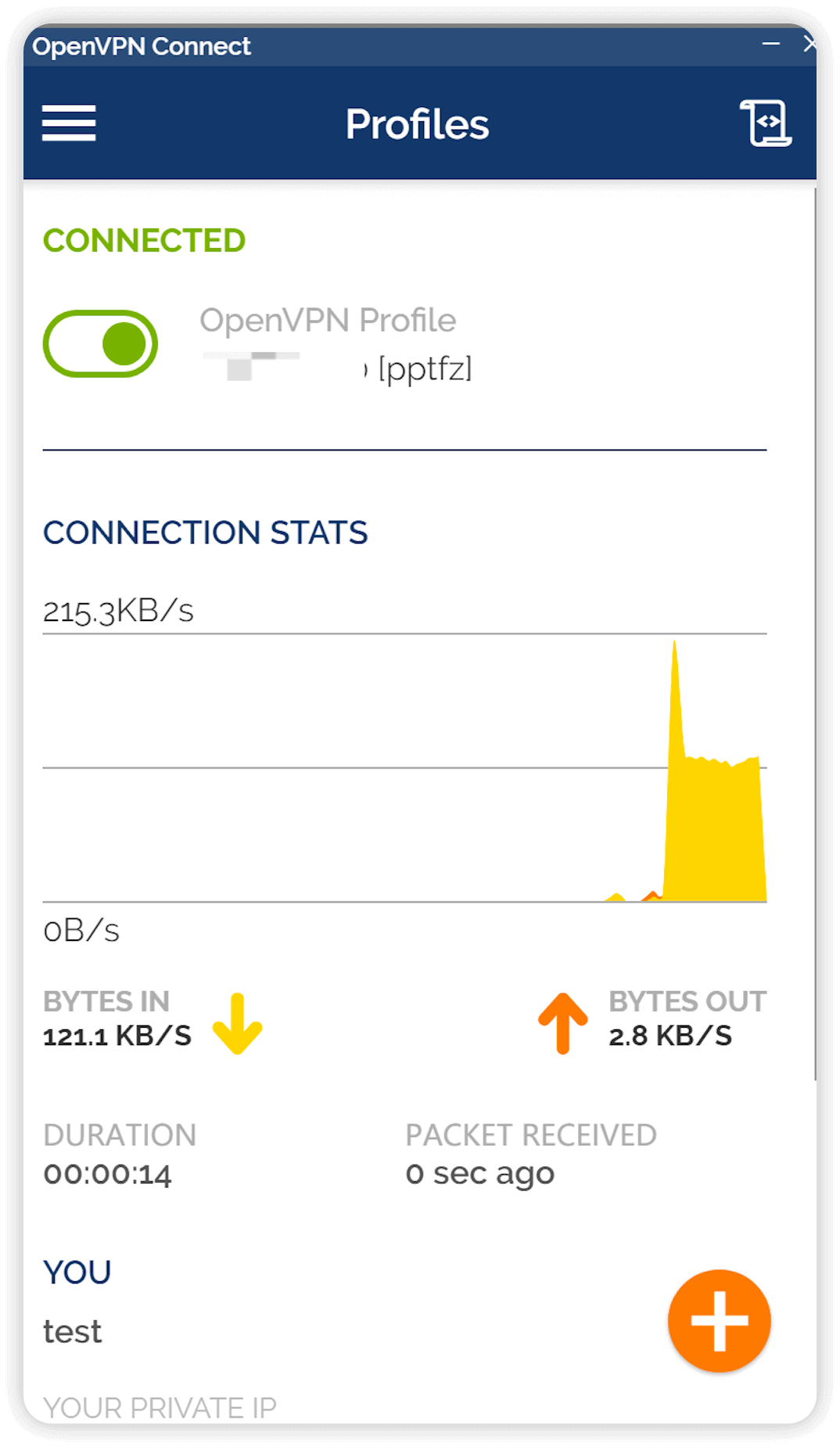
连接成功
4.云主机安全组配置说明
使用示例
假设公司代码库gitlab、上线工具jenkins等等部署在云主机中,现在只允许公司IP和openvpn IP访问
则只需要在安全组中加入以下两条规则即可
1.允许公司IP访问
2.允许OpenVPN所在机器公网IP访问
在云主机中还可以根据具体情况设置相关安全策略,包括网络ACL访问控制,安全组等等
openvpn+云主机安全组的应用��场景
如果服务所在机器是经典网络(有公网IP),则内网和公网都可以访问
如果服务所在机器是VPC网络(无公网IP),则只允许内网访问
5.脚本内容
#!/bin/bash
#
# https://github.com/Nyr/openvpn-install
#
# Copyright (c) 2013 Nyr. Released under the MIT License.
# Detect Debian users running the script with "sh" instead of bash
if readlink /proc/$$/exe | grep -q "dash"; then
echo 'This installer needs to be run with "bash", not "sh".'
exit
fi
# Discard stdin. Needed when running from an one-liner which includes a newline
read -N 999999 -t 0.001
# Detect OpenVZ 6
if [[ $(uname -r | cut -d "." -f 1) -eq 2 ]]; then
echo "The system is running an old kernel, which is incompatible with this installer."
exit
fi
# Detect OS
# $os_version variables aren't always in use, but are kept here for convenience
if grep -qs "ubuntu" /etc/os-release; then
os="ubuntu"
os_version=$(grep 'VERSION_ID' /etc/os-release | cut -d '"' -f 2 | tr -d '.')
group_name="nogroup"
elif [[ -e /etc/debian_version ]]; then
os="debian"
os_version=$(grep -oE '[0-9]+' /etc/debian_version | head -1)
group_name="nogroup"
elif [[ -e /etc/almalinux-release || -e /etc/rocky-release || -e /etc/centos-release ]]; then
os="centos"
os_version=$(grep -shoE '[0-9]+' /etc/almalinux-release /etc/rocky-release /etc/centos-release | head -1)
group_name="nobody"
elif [[ -e /etc/fedora-release ]]; then
os="fedora"
os_version=$(grep -oE '[0-9]+' /etc/fedora-release | head -1)
group_name="nobody"
else
echo "This installer seems to be running on an unsupported distribution.
Supported distros are Ubuntu, Debian, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, CentOS and Fedora."
exit
fi
if [[ "$os" == "ubuntu" && "$os_version" -lt 1804 ]]; then
echo "Ubuntu 18.04 or higher is required to use this installer.
This version of Ubuntu is too old and unsupported."
exit
fi
if [[ "$os" == "debian" && "$os_version" -lt 9 ]]; then
echo "Debian 9 or higher is required to use this installer.
This version of Debian is too old and unsupported."
exit
fi
if [[ "$os" == "centos" && "$os_version" -lt 7 ]]; then
echo "CentOS 7 or higher is required to use this installer.
This version of CentOS is too old and unsupported."
exit
fi
# Detect environments where $PATH does not include the sbin directories
if ! grep -q sbin <<< "$PATH"; then
echo '$PATH does not include sbin. Try using "su -" instead of "su".'
exit
fi
if [[ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]]; then
echo "This installer needs to be run with superuser privileges."
exit
fi
if [[ ! -e /dev/net/tun ]] || ! ( exec 7<>/dev/net/tun ) 2>/dev/null; then
echo "The system does not have the TUN device available.
TUN needs to be enabled before running this installer."
exit
fi
new_client () {
# Generates the custom client.ovpn
{
cat /etc/openvpn/server/client-common.txt
echo "<ca>"
cat /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/ca.crt
echo "</ca>"
echo "<cert>"
sed -ne '/BEGIN CERTIFICATE/,$ p' /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/issued/"$client".crt
echo "</cert>"
echo "<key>"
cat /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/private/"$client".key
echo "</key>"
echo "<tls-crypt>"
sed -ne '/BEGIN OpenVPN Static key/,$ p' /etc/openvpn/server/tc.key
echo "</tls-crypt>"
} > ~/"$client".ovpn
}
if [[ ! -e /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf ]]; then
# Detect some Debian minimal setups where neither wget nor curl are installed
if ! hash wget 2>/dev/null && ! hash curl 2>/dev/null; then
echo "Wget is required to use this installer."
read -n1 -r -p "Press any key to install Wget and continue..."
apt-get update
apt-get install -y wget
fi
clear
echo 'Welcome to this OpenVPN road warrior installer!'
# If system has a single IPv4, it is selected automatically. Else, ask the user
if [[ $(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vEc '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}') -eq 1 ]]; then
ip=$(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vE '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}')
else
number_of_ip=$(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vEc '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}')
echo
echo "Which IPv4 address should be used?"
ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vE '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | nl -s ') '
read -p "IPv4 address [1]: " ip_number
until [[ -z "$ip_number" || "$ip_number" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$ip_number" -le "$number_of_ip" ]]; do
echo "$ip_number: invalid selection."
read -p "IPv4 address [1]: " ip_number
done
[[ -z "$ip_number" ]] && ip_number="1"
ip=$(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vE '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | sed -n "$ip_number"p)
fi
# If $ip is a private IP address, the server must be behind NAT
if echo "$ip" | grep -qE '^(10\.|172\.1[6789]\.|172\.2[0-9]\.|172\.3[01]\.|192\.168)'; then
echo
echo "This server is behind NAT. What is the public IPv4 address or hostname?"
# Get public IP and sanitize with grep
get_public_ip=$(grep -m 1 -oE '^[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}$' <<< "$(wget -T 10 -t 1 -4qO- "http://ip1.dynupdate.no-ip.com/" || curl -m 10 -4Ls "http://ip1.dynupdate.no-ip.com/")")
read -p "Public IPv4 address / hostname [$get_public_ip]: " public_ip
# If the checkip service is unavailable and user didn't provide input, ask again
until [[ -n "$get_public_ip" || -n "$public_ip" ]]; do
echo "Invalid input."
read -p "Public IPv4 address / hostname: " public_ip
done
[[ -z "$public_ip" ]] && public_ip="$get_public_ip"
fi
# If system has a single IPv6, it is selected automatically
if [[ $(ip -6 addr | grep -c 'inet6 [23]') -eq 1 ]]; then
ip6=$(ip -6 addr | grep 'inet6 [23]' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '([0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}:){1,7}[0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}')
fi
# If system has multiple IPv6, ask the user to select one
if [[ $(ip -6 addr | grep -c 'inet6 [23]') -gt 1 ]]; then
number_of_ip6=$(ip -6 addr | grep -c 'inet6 [23]')
echo
echo "Which IPv6 address should be used?"
ip -6 addr | grep 'inet6 [23]' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '([0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}:){1,7}[0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}' | nl -s ') '
read -p "IPv6 address [1]: " ip6_number
until [[ -z "$ip6_number" || "$ip6_number" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$ip6_number" -le "$number_of_ip6" ]]; do
echo "$ip6_number: invalid selection."
read -p "IPv6 address [1]: " ip6_number
done
[[ -z "$ip6_number" ]] && ip6_number="1"
ip6=$(ip -6 addr | grep 'inet6 [23]' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '([0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}:){1,7}[0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}' | sed -n "$ip6_number"p)
fi
echo
echo "Which protocol should OpenVPN use?"
echo " 1) UDP (recommended)"
echo " 2) TCP"
read -p "Protocol [1]: " protocol
until [[ -z "$protocol" || "$protocol" =~ ^[12]$ ]]; do
echo "$protocol: invalid selection."
read -p "Protocol [1]: " protocol
done
case "$protocol" in
1|"")
protocol=udp
;;
2)
protocol=tcp
;;
esac
echo
echo "What port should OpenVPN listen to?"
read -p "Port [1194]: " port
until [[ -z "$port" || "$port" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$port" -le 65535 ]]; do
echo "$port: invalid port."
read -p "Port [1194]: " port
done
[[ -z "$port" ]] && port="1194"
echo
echo "Select a DNS server for the clients:"
echo " 1) Current system resolvers"
echo " 2) Google"
echo " 3) 1.1.1.1"
echo " 4) OpenDNS"
echo " 5) Quad9"
echo " 6) AdGuard"
read -p "DNS server [1]: " dns
until [[ -z "$dns" || "$dns" =~ ^[1-6]$ ]]; do
echo "$dns: invalid selection."
read -p "DNS server [1]: " dns
done
echo
echo "Enter a name for the first client:"
read -p "Name [client]: " unsanitized_client
# Allow a limited set of characters to avoid conflicts
client=$(sed 's/[^0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_-]/_/g' <<< "$unsanitized_client")
[[ -z "$client" ]] && client="client"
echo
echo "OpenVPN installation is ready to begin."
# Install a firewall if firewalld or iptables are not already available
if ! systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld.service && ! hash iptables 2>/dev/null; then
if [[ "$os" == "centos" || "$os" == "fedora" ]]; then
firewall="firewalld"
# We don't want to silently enable firewalld, so we give a subtle warning
# If the user continues, firewalld will be installed and enabled during setup
echo "firewalld, which is required to manage routing tables, will also be installed."
elif [[ "$os" == "debian" || "$os" == "ubuntu" ]]; then
# iptables is way less invasive than firewalld so no warning is given
firewall="iptables"
fi
fi
read -n1 -r -p "Press any key to continue..."
# If running inside a container, disable LimitNPROC to prevent conflicts
if systemd-detect-virt -cq; then
mkdir /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-server@server.service.d/ 2>/dev/null
echo "[Service]
LimitNPROC=infinity" > /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-server@server.service.d/disable-limitnproc.conf
fi
if [[ "$os" = "debian" || "$os" = "ubuntu" ]]; then
apt-get update
apt-get install -y openvpn openssl ca-certificates $firewall
elif [[ "$os" = "centos" ]]; then
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y openvpn openssl ca-certificates tar $firewall
else
# Else, OS must be Fedora
dnf install -y openvpn openssl ca-certificates tar $firewall
fi
# If firewalld was just installed, enable it
if [[ "$firewall" == "firewalld" ]]; then
systemctl enable --now firewalld.service
fi
# Get easy-rsa
easy_rsa_url='https://github.com/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/releases/download/v3.0.8/EasyRSA-3.0.8.tgz'
mkdir -p /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
{ wget -qO- "$easy_rsa_url" 2>/dev/null || curl -sL "$easy_rsa_url" ; } | tar xz -C /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/ --strip-components 1
chown -R root:root /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
cd /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
# Create the PKI, set up the CA and the server and client certificates
./easyrsa init-pki
./easyrsa --batch build-ca nopass
EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE=3650 ./easyrsa build-server-full server nopass
EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE=3650 ./easyrsa build-client-full "$client" nopass
EASYRSA_CRL_DAYS=3650 ./easyrsa gen-crl
# Move the stuff we need
cp pki/ca.crt pki/private/ca.key pki/issued/server.crt pki/private/server.key pki/crl.pem /etc/openvpn/server
# CRL is read with each client connection, while OpenVPN is dropped to nobody
chown nobody:"$group_name" /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
# Without +x in the directory, OpenVPN can't run a stat() on the CRL file
chmod o+x /etc/openvpn/server/
# Generate key for tls-crypt
openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/server/tc.key
# Create the DH parameters file using the predefined ffdhe2048 group
echo '-----BEGIN DH PARAMETERS-----
MIIBCAKCAQEA//////////+t+FRYortKmq/cViAnPTzx2LnFg84tNpWp4TZBFGQz
+8yTnc4kmz75fS/jY2MMddj2gbICrsRhetPfHtXV/WVhJDP1H18GbtCFY2VVPe0a
87VXE15/V8k1mE8McODmi3fipona8+/och3xWKE2rec1MKzKT0g6eXq8CrGCsyT7
YdEIqUuyyOP7uWrat2DX9GgdT0Kj3jlN9K5W7edjcrsZCwenyO4KbXCeAvzhzffi
7MA0BM0oNC9hkXL+nOmFg/+OTxIy7vKBg8P+OxtMb61zO7X8vC7CIAXFjvGDfRaD
ssbzSibBsu/6iGtCOGEoXJf//////////wIBAg==
-----END DH PARAMETERS-----' > /etc/openvpn/server/dh.pem
# Generate server.conf
echo "local $ip
port $port
proto $protocol
dev tun
ca ca.crt
cert server.crt
key server.key
dh dh.pem
auth SHA512
tls-crypt tc.key
topology subnet
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0" > /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
# IPv6
if [[ -z "$ip6" ]]; then
echo 'push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
else
echo 'server-ipv6 fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "redirect-gateway def1 ipv6 bypass-dhcp"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
fi
echo 'ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
# DNS
case "$dns" in
1|"")
# Locate the proper resolv.conf
# Needed for systems running systemd-resolved
if grep -q '^nameserver 127.0.0.53' "/etc/resolv.conf"; then
resolv_conf="/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf"
else
resolv_conf="/etc/resolv.conf"
fi
# Obtain the resolvers from resolv.conf and use them for OpenVPN
grep -v '^#\|^;' "$resolv_conf" | grep '^nameserver' | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | while read line; do
echo "push \"dhcp-option DNS $line\"" >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
done
;;
2)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.4.4"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
3)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 1.1.1.1"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 1.0.0.1"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
4)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
5)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 9.9.9.9"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 149.112.112.112"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
6)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 94.140.14.14"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 94.140.15.15"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
esac
echo "keepalive 10 120
cipher AES-256-CBC
user nobody
group $group_name
persist-key
persist-tun
verb 3
crl-verify crl.pem" >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
if [[ "$protocol" = "udp" ]]; then
echo "explicit-exit-notify" >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
fi
# Enable net.ipv4.ip_forward for the system
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward=1' > /etc/sysctl.d/99-openvpn-forward.conf
# Enable without waiting for a reboot or service restart
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
if [[ -n "$ip6" ]]; then
# Enable net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding for the system
echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1" >> /etc/sysctl.d/99-openvpn-forward.conf
# Enable without waiting for a reboot or service restart
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/forwarding
fi
if systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld.service; then
# Using both permanent and not permanent rules to avoid a firewalld
# reload.
# We don't use --add-service=openvpn because that would only work with
# the default port and protocol.
firewall-cmd --add-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --add-source=10.8.0.0/24
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-source=10.8.0.0/24
# Set NAT for the VPN subnet
firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
if [[ -n "$ip6" ]]; then
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --add-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
fi
else
# Create a service to set up persistent iptables rules
iptables_path=$(command -v iptables)
ip6tables_path=$(command -v ip6tables)
# nf_tables is not available as standard in OVZ kernels. So use iptables-legacy
# if we are in OVZ, with a nf_tables backend and iptables-legacy is available.
if [[ $(systemd-detect-virt) == "openvz" ]] && readlink -f "$(command -v iptables)" | grep -q "nft" && hash iptables-legacy 2>/dev/null; then
iptables_path=$(command -v iptables-legacy)
ip6tables_path=$(command -v ip6tables-legacy)
fi
echo "[Unit]
Before=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=$iptables_path -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to $ip
ExecStart=$iptables_path -I INPUT -p $protocol --dport $port -j ACCEPT
ExecStart=$iptables_path -I FORWARD -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j ACCEPT
ExecStart=$iptables_path -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$iptables_path -t nat -D POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to $ip
ExecStop=$iptables_path -D INPUT -p $protocol --dport $port -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$iptables_path -D FORWARD -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$iptables_path -D FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT" > /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
if [[ -n "$ip6" ]]; then
echo "ExecStart=$ip6tables_path -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to $ip6
ExecStart=$ip6tables_path -I FORWARD -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j ACCEPT
ExecStart=$ip6tables_path -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$ip6tables_path -t nat -D POSTROUTING -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to $ip6
ExecStop=$ip6tables_path -D FORWARD -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$ip6tables_path -D FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT" >> /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
fi
echo "RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target" >> /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
systemctl enable --now openvpn-iptables.service
fi
# If SELinux is enabled and a custom port was selected, we need this
if sestatus 2>/dev/null | grep "Current mode" | grep -q "enforcing" && [[ "$port" != 1194 ]]; then
# Install semanage if not already present
if ! hash semanage 2>/dev/null; then
if [[ "$os_version" -eq 7 ]]; then
# Centos 7
yum install -y policycoreutils-python
else
# CentOS 8 or Fedora
dnf install -y policycoreutils-python-utils
fi
fi
semanage port -a -t openvpn_port_t -p "$protocol" "$port"
fi
# If the server is behind NAT, use the correct IP address
[[ -n "$public_ip" ]] && ip="$public_ip"
# client-common.txt is created so we have a template to add further users later
echo "client
dev tun
proto $protocol
remote $ip $port
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
remote-cert-tls server
auth SHA512
cipher AES-256-CBC
ignore-unknown-option block-outside-dns
block-outside-dns
verb 3" > /etc/openvpn/server/client-common.txt
# Enable and start the OpenVPN service
systemctl enable --now openvpn-server@server.service
# Generates the custom client.ovpn
new_client
echo
echo "Finished!"
echo
echo "The client configuration is available in:" ~/"$client.ovpn"
echo "New clients can be added by running this script again."
else
clear
echo "OpenVPN is already installed."
echo
echo "Select an option:"
echo " 1) Add a new client"
echo " 2) Revoke an existing client"
echo " 3) Remove OpenVPN"
echo " 4) Exit"
read -p "Option: " option
until [[ "$option" =~ ^[1-4]$ ]]; do
echo "$option: invalid selection."
read -p "Option: " option
done
case "$option" in
1)
echo
echo "Provide a name for the client:"
read -p "Name: " unsanitized_client
client=$(sed 's/[^0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_-]/_/g' <<< "$unsanitized_client")
while [[ -z "$client" || -e /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/issued/"$client".crt ]]; do
echo "$client: invalid name."
read -p "Name: " unsanitized_client
client=$(sed 's/[^0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_-]/_/g' <<< "$unsanitized_client")
done
cd /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE=3650 ./easyrsa build-client-full "$client" nopass
# Generates the custom client.ovpn
new_client
echo
echo "$client added. Configuration available in:" ~/"$client.ovpn"
exit
;;
2)
# This option could be documented a bit better and maybe even be simplified
# ...but what can I say, I want some sleep too
number_of_clients=$(tail -n +2 /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | grep -c "^V")
if [[ "$number_of_clients" = 0 ]]; then
echo
echo "There are no existing clients!"
exit
fi
echo
echo "Select the client to revoke:"
tail -n +2 /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | grep "^V" | cut -d '=' -f 2 | nl -s ') '
read -p "Client: " client_number
until [[ "$client_number" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$client_number" -le "$number_of_clients" ]]; do
echo "$client_number: invalid selection."
read -p "Client: " client_number
done
client=$(tail -n +2 /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | grep "^V" | cut -d '=' -f 2 | sed -n "$client_number"p)
echo
read -p "Confirm $client revocation? [y/N]: " revoke
until [[ "$revoke" =~ ^[yYnN]*$ ]]; do
echo "$revoke: invalid selection."
read -p "Confirm $client revocation? [y/N]: " revoke
done
if [[ "$revoke" =~ ^[yY]$ ]]; then
cd /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
./easyrsa --batch revoke "$client"
EASYRSA_CRL_DAYS=3650 ./easyrsa gen-crl
rm -f /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
cp /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/crl.pem /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
# CRL is read with each client connection, when OpenVPN is dropped to nobody
chown nobody:"$group_name" /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
echo
echo "$client revoked!"
else
echo
echo "$client revocation aborted!"
fi
exit
;;
3)
echo
read -p "Confirm OpenVPN removal? [y/N]: " remove
until [[ "$remove" =~ ^[yYnN]*$ ]]; do
echo "$remove: invalid selection."
read -p "Confirm OpenVPN removal? [y/N]: " remove
done
if [[ "$remove" =~ ^[yY]$ ]]; then
port=$(grep '^port ' /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf | cut -d " " -f 2)
protocol=$(grep '^proto ' /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf | cut -d " " -f 2)
if systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld.service; then
ip=$(firewall-cmd --direct --get-rules ipv4 nat POSTROUTING | grep '\-s 10.8.0.0/24 '"'"'!'"'"' -d 10.8.0.0/24' | grep -oE '[^ ]+$')
# Using both permanent and not permanent rules to avoid a firewalld reload.
firewall-cmd --remove-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --remove-source=10.8.0.0/24
firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --remove-source=10.8.0.0/24
firewall-cmd --direct --remove-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --remove-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
if grep -qs "server-ipv6" /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf; then
ip6=$(firewall-cmd --direct --get-rules ipv6 nat POSTROUTING | grep '\-s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 '"'"'!'"'"' -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64' | grep -oE '[^ ]+$')
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --remove-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --remove-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --direct --remove-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --remove-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
fi
else
systemctl disable --now openvpn-iptables.service
rm -f /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
fi
if sestatus 2>/dev/null | grep "Current mode" | grep -q "enforcing" && [[ "$port" != 1194 ]]; then
semanage port -d -t openvpn_port_t -p "$protocol" "$port"
fi
systemctl disable --now openvpn-server@server.service
rm -f /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-server@server.service.d/disable-limitnproc.conf
rm -f /etc/sysctl.d/99-openvpn-forward.conf
if [[ "$os" = "debian" || "$os" = "ubuntu" ]]; then
rm -rf /etc/openvpn/server
apt-get remove --purge -y openvpn
else
# Else, OS must be CentOS or Fedora
yum remove -y openvpn
rm -rf /etc/openvpn/server
fi
echo
echo "OpenVPN removed!"
else
echo
echo "OpenVPN removal aborted!"
fi
exit
;;
4)
exit
;;
esac
fi