[toc]
Linux权限总结
Linux普通权限
文件权限查看
$ ll
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 7570 Aug 4 13:15 install.log.syslog
drwxr-xr-x 9 root root 4096 Aug 8 12:07 test
用户分组权限概念
| -rw-r--r-- | 权限 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 第1位 | - | 表示文件类型,- 表示普通文件,d 表示目录 |
| 第2-4位 | rw- | 表示文件所有者权限 |
| 第5-7位 | r-- | 表示文件所属组权限 |
| 第8-10位 | r-- | 表示文件其他人权限 |
权限位含义
| 权限位 | 含义 |
|---|---|
r | 读 |
w | 写 |
x | 执行 |
权限位数字表示法
读+写+执行 = 4+2+1=7
| 权限位 | 数字 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
r | 4 | 读 |
w | 2 | 写 |
x | 1 | 执行 |
权限对文件及目录含义
文件rwx权限
| 权限位 | 含义 |
|---|---|
r | 读取文件内容 |
w | 修改文件内容需要r权限配合,只有w权限的时候强制保存退出会导致源文件内容丢失 |
x | 表示是否执行,需要r权限配合 |
目录rwx权限
| 权限位 | 含义 |
|---|---|
r | 查看目录内容,相当于 ls ,需要x权限配合 |
w | 是否能删除目录内容,是否能在目录中创建文件、重命名目录中的文件 |
x | 是否能进入到目录,是否能查看目录中文件的属性 |
linux特殊权限
suid
-
用户在运行命令的时候相当于root用户
-
设置方法
u+s
示例说明
1.普通用户 pptfz 无法使用 less 命令查看系统日志 /var/log/messages
[pptfz@pptfz ~]$ less /var/log/messages
/var/log/messages: Permission denied
2.给 /usr/bin/less 设置 suid
设置 suid 后文件权限所有者处就变为 rws ,多了一个 s 权限,并且文件底色变成了红色
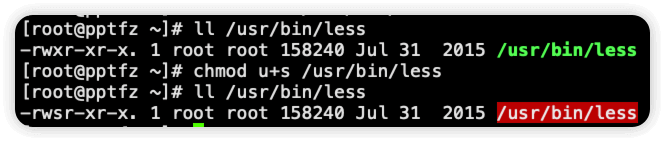
使用命令 stat 查看文件属性,此时文件权限位是 4755
$ stat /usr/bin/less
File: ‘/usr/bin/less’
Size: 158240 Blocks: 312 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 9826 Links: 1
Access: (4755/-rwsr-xr-x) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2024-08-27 18:31:48.699665151 +0800
Modify: 2015-07-31 07:50:42.000000000 +0800
Change: 2024-08-27 18:34:26.037784186 +0800
Birth: -
3.为 /usr/bin/less 设置 suid 后 www 用户就可以查看系统日志了
[pptfz@pptfz ~]$ less /var/log/messages
Feb 11 03:48:01 tencent systemd: Started Session 193698 of user root.
Feb 11 03:49:01 tencent systemd: Started Session 193699 of user root.
Feb 11 03:50:01 tencent systemd: Started Session 193701 of user root.
......
sgid
-
用户若对此目录具有r与x的权限时,该用户能够进入此目录
-
用户在此目录下的有效用户组将会变成该目录的用户组
-
若用户在此目录下具有w的权限,则用户创建新文件的用户组与此目录的用户组相同
-
设置方法
g+s
示例说明
1.普通用户 pptfz 对 /tmp 目录有 777 权限,在没有设置 /tmp 的 sgid 时,pptfz 用户在此创建的文件和目录属组是本身,即 pptfz
[pptfz@pptfz /tmp]$ ll
drwxrwxr-x 2 pptfz pptfz 4096 Aug 27 18:42 test-dir
-rw-rw-r-- 1 pptfz pptfz 0 Aug 27 18:42 test-file
2.为 /tmp 目录设置 sgid 后,pptfz 用户在 /tmp 下创建的文件和目录属组就是 root
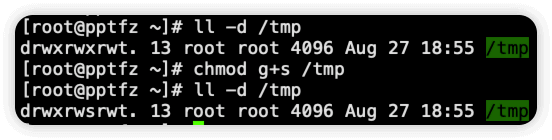
[pptfz@pptfz /tmp]$ ll
drwxrwsr-x 2 pptfz root 4096 Aug 27 18:54 test-dir
-rw-rw-r-- 1 pptfz root 0 Aug 27 18:54 test-file
sbit sticky粘滞位
-
当一个用户对某目录是具有用户组或其他人的身份,并具有w权限(即具有写入的权限时),这表明该用户可以对该目录下任何人新建的目录或文件进行删除、移动、重命名等操作。不过,如果该目录具有SBIT权限时,则仅有文件属主和root才能删除、移动、重命��名此文件,普通用户无法删除该目录下不属于自己的文件
-
设置方法
o+t
示例说明
1.在没有设置 sbit 时,普通用户 www 可以删除 /tmp 下属主属组不是自己的文件和目录
取消 /tmp 目录的 sbit
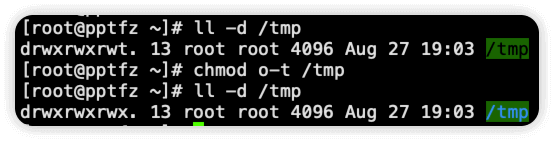
以 root 用户创建文件和目录,可以看到此时文件 test-file 和目录 test-dir 属主和属组都是 root
[root@pptfz ~]# touch /tmp/test-file
[root@pptfz ~]# mkdir /tmp/test-dir
[root@pptfz ~]# ll /tmp/test-file
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 27 19:08 /tmp/test-file
[root@pptfz ~]# ll -d /tmp/test-dir/
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 27 19:08 /tmp/test-dir/
以 pptfz 用户删除test-file 和 test-dir ,发现是可以删除的
[pptfz@pptfz /tmp]$ rm -rf test-file test-dir/
2.设置 sbit 后,www 用户只能删除文件所有者是自己的文件
设置 sbit 后,文件权限其他人处变为了 rwt
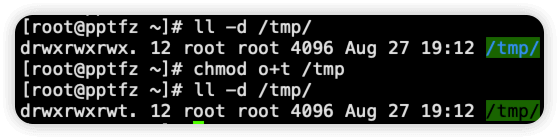
使用命令 stat 查看 /tmp 权限,此时为 1777
$ stat /tmp
File: ‘/tmp’
Size: 4096 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 directory
Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 8193 Links: 12
Access: (1777/drwxrwxrwt) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2024-08-27 19:10:34.314383681 +0800
Modify: 2024-08-27 19:12:57.462035180 +0800
Change: 2024-08-27 19:13:05.718303481 +0800
Birth: -
再以 root 用户创建文件和目录,可以看到此时文件 test-file 和目录 test-dir 属主和属组都是 root
[root@pptfz ~]# touch /tmp/test-file
[root@pptfz ~]# mkdir /tmp/test-dir
[root@pptfz ~]# ll /tmp/test-file
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 27 19:16 /tmp/test-file
[root@pptfz ~]# ll -d /tmp/test-dir/
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 27 19:16 /tmp/test-dir/
此时, pptfz 用户无法删除文件所有者不是自己的文件
[pptfz@pptfz /tmp]$ rm -rf test-file test-dir/
rm: cannot remove ‘test-file’: Operation not permitted
rm: cannot remove ‘test-dir/’: Operation not permitted
linux隐藏权限
权限位
| 权限位 | 说明 |
|---|---|
a (append 追加) | 只能追加和查看,其他操作都无法执行 |
i (immutable 不可变的) | 不可变,只能查看,其他操作都无法执行 |
设置隐藏权限命令 chattr
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
chattr + | 增加 |
chattr - | 取消 |
为文件添加隐藏权限 a 后,可以看到,文件只能被追加和查看,其他操作无法执行
# 设置隐藏权限
$ chattr +a test.txt
# 只能追加
$ echo 123 >> test.txt
# 不能重定向
$ echo 678 > test.txt
-bash: test.txt: Operation not permitted
# 不能删除
$ rm -rf test.txt
rm: cannot remove ‘test.txt’: Operation not permitted
# 不能移动
$ mv test.txt abc.txt
mv: cannot move ‘test.txt’ to ‘abc.txt’: Operation not permitted
为文件添加隐藏权限 i 后,可以看到,文件只能被查看,其他操作无法执行
# 设置隐藏权限
$ chattr +i test.txt
# 不能追加
$ echo 123 >> test.txt
-bash: test.txt: Operation not permitted
# 不能重定向
$ echo 678 > test.txt
-bash: test.txt: Operation not permitted
# 不能删除
$ rm -rf test.txt
rm: cannot remove ‘test.txt’: Operation not permitted
# 不能移动
$ mv test.txt abc.txt
mv: cannot move ‘test.txt’ to ‘abc.txt’: Operation not permitted
# 只能查看
$ cat test.txt
123
查看隐藏权限 lsattr
$ lsattr test.txt
----i--------e-- test.txt
FACL Filesystem Acess
FACL是一种权限分配之外的普遍方式,例如,默认情况下你需要确认3个权限组,owner 、group 、other ,而使用FACL,利用文件扩展属性保存额外的访问控制权限,你可以增加权限给其他用户或组,而不单只是简单的other或者是拥有者不存在的组别,可以允许指定的用户拥有写权限而不再是让他们整个组拥有写权限
FACL格式
[u|g]:[用户名|组名]:权限 文件
例如 u:hehe:rwx file ,意思是对于文件 file ,用户hehe 有 rwx 权限
设置FACL setfacl
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
-m | 设置FACL权限 |
-x | 取消FACL权限 |
-R | 递归设置,-R 需要写在 -m 选项前边 |
-b | 删除全部FACL权限 |
设置FACL示例
/test 目录权限为 750 ,其他人没有任何权限,但是现在想让用户 pptfz 拥有 rx 权限
[root@pptfz ~]# mkdir /test
[root@pptfz ~]# ll -d /test/
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 27 19:30 /test/
[root@pptfz ~]# chmod 750 /test/
[root@pptfz ~]# ll -d /test/
drwxr-x--- 2 root root 4096 Aug 27 19:30 /test/
1.没有设置FACL之前,pptfz 用户无法进入 /test 目录,无法查看 /test 目录内容
[pptfz@pptfz ~]$ cd /test/
-bash: cd: /test/: Permission denied
[pptfz@pptfz ~]$ ls /test
ls: cannot open directory /test: Permission denied
2.为 pptfz 用户设置 /test 的FACL
setfacl -m u:pptfz:r-x /test
[root@pptfz ~]# ll -d /test/
drwxr-x--- 2 root root 4096 Aug 27 19:30 /test/
[root@pptfz ~]# setfacl -m u:pptfz:r-x /test
[root@pptfz ~]# ll -d /test/
drwxr-x---+ 2 root root 4096 Aug 27 19:30 /test/
3.验证,设置FACL之后,只有 pptfz 这一个用户对 /test 目录拥有 rx 权限,其他普通用户没有权限
# pptfz用户对/test目录有权限
[pptfz@pptfz ~]$ cd /test/
[pptfz@pptfz /test]$ cd
[pptfz@pptfz ~]$ ls /test/
# test用户对/test目录没有权限
[test@pptfz ~]$ cd /test/
-bash: cd: /test/: Permission denied
[test@pptfz ~]$ ls /test/
ls: cannot open directory /test/: Permission denied
取消FACL
取消FACL,使用 -x 选项,与设置FACL不同,取消的时候格式中不用再加权限
setfacl -x u:pptfz /test/
查看FACL getfacl
没有设置FACL前
$ getfacl /test
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: test
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
group::r-x
mask::r-x
other::---
设置FACL后,可以看到多了一行 user:pptfz:r-x
$ getfacl /test
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: test
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:pptfz:r-x
group::r-x
mask::r-x
other::---