[toc]
shell简介
1.什么是shell
Shell 是一个用 C 语言编写的程序,它是用户使用 Linux 的桥梁。Shell 既是一种命令语言,又是一种程序设计语言。
Shell 是指一种应用程序,这个应用程序提供了一个界面,用户通过这个界面访问操作系统内核的服务。
Ken Thompson 的 sh 是第一种 Unix Shell,Windows Explorer 是一个典型的图形界面Shell。
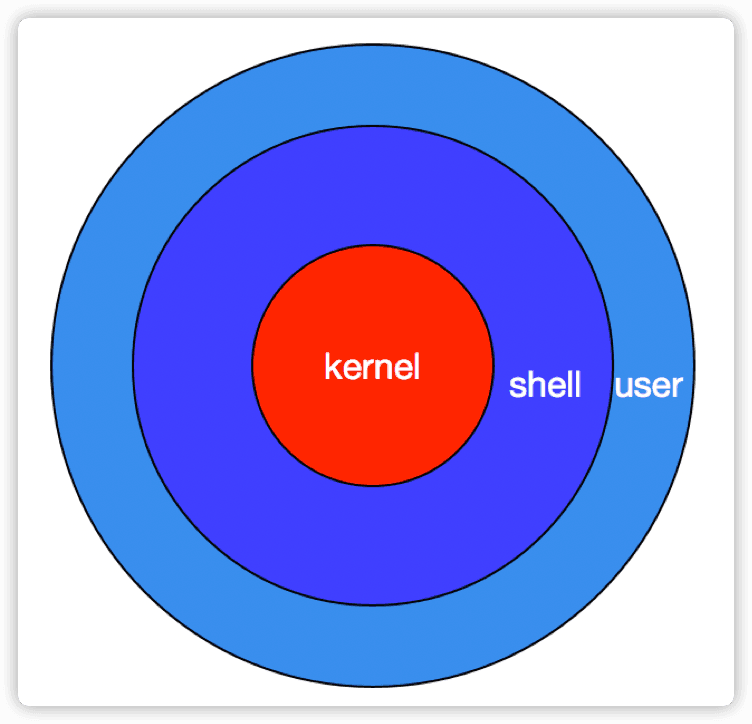
kernel:为�软件服务,接收用户或软件指令驱动硬件,完成工作
shell:命令解释器
user:用户接口,对接用户
上图可以看出,shell在操作系统中起到了承接用户和系统内核的作用。那为什么不直接用户对内核呢?
原因很简单,因为内核处理的都是二进制,而用户处理的都是高级语言。
Shell 脚本
Shell 脚本(shell script),是一种为 shell 编写的脚本程序。
业界所说的 shell 通常都是指 shell 脚本,但是shell 和 shell script 是两个不同的概念。
Shell 环境
Shell 编程跟 JavaScript、php 编程一样,只要有一个能编写代码的文本编辑器和一个能解释执行的脚本解释器就可以了。
Linux 的 Shell 种类众多,常见的有:
- Bourne Shell(/usr/bin/sh或/bin/sh)
- Bourne Again Shell(/bin/bash)
- C Shell(/usr/bin/csh)
- K Shell(/usr/bin/ksh)
- Shell for Root(/sbin/sh)
- ……
在一般情况下,人们并不区分 Bourne Shell 和 Bourne Again Shell,所以,像 #!/bin/sh,它同样也可以改为 #!/bin/bash。
#! 是告诉系统其后路径所指定的程序即是解释此脚本文件的 Shell 程序。
2.shell分类
2.1 交互分类
2.1.1 交互式shell
交互式:顾名思义就是 shell 与用户存在交互,
用户登录后,在终端上输入命令,shell 立即执行用户提交的命令。
当用户退出后,shell 也终止了。
2.1.2 非交互式shell
非交互式:即 shell 与用户不存在交互,而是以 shell script 的方式执行的。
shell 读取存放在文件中的命令, 并且执行它们,类似如下
cat > test.sh <<EOF
a
b
c
EOF
2.2 登陆分类
2.2.1 登陆式shell
- 登录 shell 是指需要用户名、密码登录后进入的 shell,或者通过
--login选项生成的 shell - su - username
2.2.2 非登陆式shell
-
非登录式 shell 是指不需要输入用户名和密码即可打开的 shell,比如输入命令
bash或者sh就能进入一个全新的非登录 shell -
图形终端下打开的命令窗口
-
自动执行的shell脚本
-
su username
2.2.3 区分登陆式shell和非登陆式shell
区分方法一 可以通过查看 $0 的值,登录式 shell 返回 -bash,而非登录式 shell 返回的是 bash
#通过终端输入用户名和密码登录的登陆式shell
$ echo $0
-bash
#通过su username登陆的非登陆式shell
$ su www
$ echo $0
bash
区分方法二 执行exit命令和logout命令
执行 exit 命令, 退出的 shell 可以是登录式shell 或者 非登录式 shell ;
执行 logout 命令,则只能退出登录式 shell,不能退出非登录式 shell
执行exit命令
#通过终端输入用户名和密码登录的登陆式shell
$ exit
登出
Connection to 10.0.0.10 closed.
#通过su username登陆的非登��陆式shell
$ su www
[www@test1 root]$ exit
exit
执行logout命令
#通过终端输入用户名和密码登录的登陆式shell
$ logout
Connection to 10.0.0.10 closed.
#通过su username登陆的非登陆式shell
$ logout
bash: logout: 不是登录shell: 使用 `exit'
3.shell的配置文件
登录式shell 读取配置 文件过程: /etc/profile –> /etc/profile.d/*.sh –> ~ /.bash_profile –> ~ /bashrc –> /etc/bashrc
非登录式shell 读取配置 文件过程: ~ /.bashrc –> /etc/bashrc –> /etc/prodile.d/*.sh
3.1 bash的配置文件
- 全局配置文件
- /etc/profile
- /etc/profile.d/*
- /etc/bashrc
- 个人配置文件
- ~/.bash_profile
- ~/.bashrc
profile类文件作用
- 1.设定环境变量
- 2.运行命令或脚本(登录时运行的脚本)
bashrc类文件配置作用
- 1.设定本地变量
- 2.定义命令别名
3.2 各shell读取配置文件过程
3.2.1 bash
1、交互式的登录shell (bash –il test.sh) 载入的信息: /etc/profile ~/.bash_profile( -> ~/.bashrc -> /etc/bashrc) ~/.bash_login ~/.profile
2、非交互式的登录shell (bash –l test.sh) 载入的信息: /etc/profile ~/.bash_profile ( -> ~/.bashrc -> /etc/bashrc) ~/.bash_login ~/.profile $BASH_ENV
3、交互式的非登录shell (bash –i test.sh) 载入的信息: ~/.bashrc ( -> /etc/bashrc)
4、非交互式的非登录shell (bash test.sh) 载入的信息: $BASH_ENV
3.2.2 sh
1、交互式的登录shell (sh –il test.sh) 载入的信息: /etc/profile ~/.profile
2、非交互式的登录shell (sh –l test.sh) 载入的信息: /etc/profile ~/.profile
3、交互式的非登录shell (sh –i test.sh) 载入的信息: $ENV
4、非交互式的非登录shell (sh test.sh) 载入的信息: nothing
综上可知, 交互/非交互/登录/非登录,这四种 shell 主要区别在于:是否载入相关配置文件!
这些配置的载入与否,导致了 Linux 很多默认选项的差异。